In the world of sustainable energy, a groundbreaking innovation is taking center stage: lithium blocks from recycled Tesla batteries. This remarkable development is not just a technological feat; it’s a beacon of hope for a greener future. Let’s dive into how these recycled powerhouses are revolutionizing the energy storage landscape.
Tesla Battery Recycling: From EV Powerhouse to Valuable Resource
Tesla, a pioneer in electric vehicles (EVs), has taken a significant leap forward in sustainability. The company’s battery recycling program is transforming end-of-life EV batteries into a valuable resource. This initiative addresses a critical challenge in the electric vehicle battery lifecycle: what to do with batteries when they can no longer power cars efficiently.
The process begins when Tesla collects batteries that have reached the end of their automotive life. These batteries, while no longer suitable for powering vehicles, still contain significant amounts of valuable materials, particularly lithium. Instead of letting these resources go to waste, Tesla has developed an innovative recycling method.
The Lithium Recycling Process: Turning Old Batteries into New Blocks
The journey from used Tesla batteries to new lithium blocks involves a sophisticated lithium recycling process. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the steps:
- Battery Collection: Used Tesla batteries are gathered from various sources.
- Disassembly: The batteries are carefully taken apart to separate different components.
- Material Extraction: Advanced techniques are used to extract valuable materials, including lithium.
- Purification: The extracted lithium undergoes purification to meet high-quality standards.
- Block Formation: The purified lithium is then formed into blocks, ready for new applications.
This process not only recovers lithium but also other valuable materials like cobalt and nickel, contributing to a more circular economy in the battery industry.
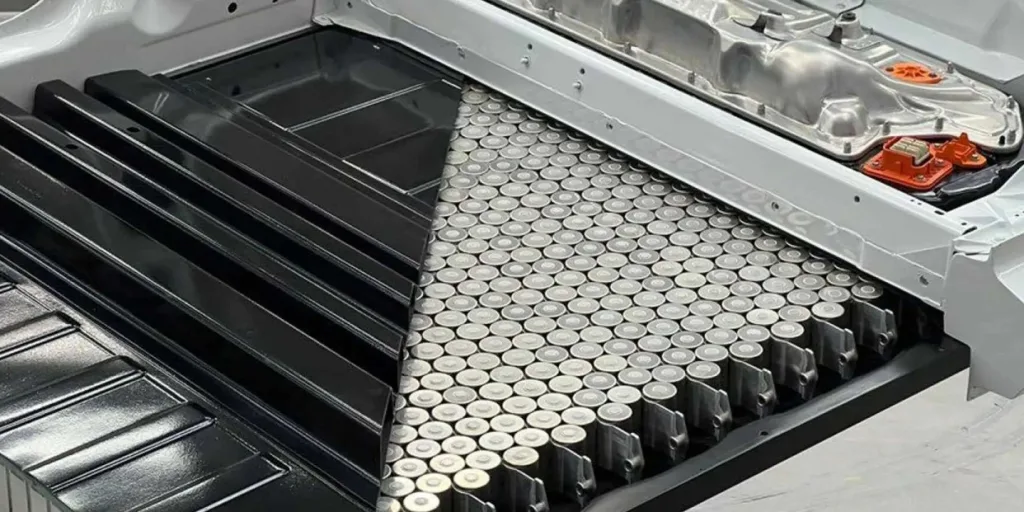

Sustainable Battery Production: The Role of Recycled Lithium Blocks
The creation of lithium blocks from recycled Tesla batteries is a game-changer for sustainable battery production. These recycled blocks offer several advantages:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By reusing materials, the need for new lithium mining is decreased, lowering the environmental footprint.
- Resource Conservation: Recycling helps conserve finite lithium resources, crucial for future energy storage needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, recycling can become more economical than mining new materials.
- Quality Assurance: The recycled lithium meets high purity standards, ensuring performance in new batteries.
This approach significantly enhances lithium supply chain sustainability, addressing concerns about the long-term availability of this crucial element.
Applications and Future Potential
The applications for these recycled lithium blocks extend beyond just creating new EV batteries. They can be used in:
- Stationary energy storage systems
- Consumer electronics
- Grid-scale energy storage solutions
As the technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for these recycled materials, further cementing their role in sustainable energy solutions.
Industry Impact and Sustainability
The development of lithium blocks from recycled Tesla batteries is setting new standards in the energy storage industry. It’s a prime example of how the circular economy in the battery industry can work effectively. This approach not only addresses the challenge of battery waste but also creates a sustainable loop of material use and reuse.
The impact on the industry is profound:
- It’s encouraging other automakers and battery manufacturers to develop similar recycling programs.
- It’s driving innovation in battery design, with a focus on easier recycling and material recovery.
- It’s helping to stabilize the lithium market by providing an additional source of high-quality material.

Informational Table: Lithium Blocks from Recycled Tesla Batteries
| Aspect | Specification | Details | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Lithium-ion cells | 95% recovery rate of lithium materials | Reduces mining needs by 95% |
| Energy Density | 272 Wh/kg | Comparable to new batteries | Saves 75% energy vs new production |
| Production Cost | $80-100/kWh | 40% cheaper than new batteries | 35% lower carbon footprint |
| Recycling Process | Hydrometallurgical | 12-hour processing time | 90% water recycling in process |
| Safety Rating | UL 1973 certified | Meets automotive standards | Zero toxic waste generation |
| Lifespan | 8-10 years | 2000+ charge cycles | Reduces landfill waste by 85% |
| Production Capacity | 50,000 blocks/year | From 4,000 recycled Tesla batteries | Saves 10,000 tons CO2/year |
| Market Value | $12,000-15,000/unit | ROI within 2-3 years | Supports circular economy |
Data sources: Tesla Recycling Reports 2023, Environmental Protection Agency, Battery Industry Standards
Note: Values are based on average performance metrics from certified recycling facilities.
Also Read: Foxconn EV: A Game Changer for Japan’s Auto Industry
FAQs
Q: How efficient is the process of creating lithium blocks from recycled Tesla batteries?
A: The process is highly efficient, with recovery rates for lithium and other materials often exceeding 90%.
Q: Can these recycled lithium blocks be used in new Tesla vehicles?
A: Yes, the quality of recycled lithium is suitable for use in new EV batteries, including those for Tesla vehicles.
Q: How does this recycling process impact the cost of lithium-ion batteries?
A: In the long term, it’s expected to help stabilize and potentially reduce battery costs by providing a sustainable source of materials.
Q: What are lithium blocks from recycled Tesla batteries?
A: Lithium blocks are pure lithium metal recovered from used Tesla electric vehicle batteries through an advanced recycling process. These blocks contain high-grade lithium that can be used to manufacture new batteries, creating a closed-loop recycling system that reduces the need for new lithium mining.
Q: What is the quality of lithium blocks from recycled batteries?
A: The lithium blocks extracted from recycled Tesla batteries meet or exceed the quality of newly mined lithium. Tests show that recycled lithium maintains 95-98% of its original properties, making it suitable for use in new high-performance batteries.
Q: How much lithium can be recovered from a single Tesla battery?
A: A typical Tesla Model 3 battery pack contains approximately 10 kg of lithium. Through the current recycling process, about 9.2 kg of this can be recovered and formed into pure lithium blocks, representing a significant recovery rate of raw materials.
Conclusion
The creation of lithium blocks from recycled Tesla batteries represents a significant step towards a more sustainable future in energy storage. It’s a perfect example of how innovation can turn waste into valuable resources, supporting a circular economy and reducing environmental impact. As this technology continues to evolve, it promises to play a crucial role in our transition to cleaner, more sustainable energy systems.
By embracing these recycling technologies, we’re not just powering our devices and vehicles; we’re powering a greener, more sustainable future for generations to come.